If you’re looking to lose weight and keep it off, the Paleo diet might be right for you. By eating nutrient-dense, whole foods, you can reduce your caloric intake while still feeling full and satisfied.
I. Introduction

A. Explanation of the paleo diet
The paleo diet, also known as the Paleolithic or caveman diet, is a modern nutritional approach based on the eating habits of our hunter-gatherer ancestors. It is a diet that focuses on consuming whole, unprocessed foods that our bodies are adapted to digest. The premise behind the paleo diet is that our modern diet, which includes highly processed foods and grains, is contributing to the development of chronic diseases. Proponents of the paleo diet believe that by returning to a diet similar to that of our ancestors, we can improve our overall health and well-being. In this blog post, we will explore the key principles of the paleo diet and the potential benefits it may offer.
B. Brief history of the paleo diet
The paleo diet, also known as the Paleolithic diet or the caveman diet, is a modern nutritional plan based on the presumed diet of humans during the Paleolithic era. The Paleolithic era is the period from approximately 2.5 million to 10,000 years ago. The idea behind the paleo diet is that our bodies are not adapted to the modern agricultural diet that emerged around 10,000 years ago with the advent of farming, and that the human body has not had enough time to evolve to handle these foods properly.
The modern version of the paleo diet was developed in the 1970s by gastroenterologist Walter L. Voegtlin, who believed that a diet based on the foods our Paleolithic ancestors ate would improve our health and help us avoid modern-day diseases. The paleo diet gained popularity in the 2000s, and today it is one of the most popular dietary trends.
C. Explanation of the benefits of the paleo diet
The paleo diet has been credited with a number of benefits, both in terms of improving overall health and aiding in weight loss. Here are some of the benefits that have been associated with following a paleo diet:
- Improved digestion: By cutting out processed foods and focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, the paleo diet can help promote better digestion.
- Increased energy: Many people report feeling more energized and alert after starting a paleo diet, possibly due to the elimination of sugar and refined carbohydrates.
- Improved blood sugar control: By eliminating sugar and refined carbs, the paleo diet can help regulate blood sugar levels and may be particularly helpful for those with type 2 diabetes.
- Reduced inflammation: The paleo diet is rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation throughout the body.
- Weight loss: The paleo diet emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods and eliminates processed and high-calorie foods, which can help with weight loss.
- Improved heart health: The paleo diet encourages the consumption of healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, which can improve heart health.
- Food sourcing and sustainability: The paleo diet emphasizes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods and encourages the use of sustainably-sourced, locally-produced foods.
It’s important to note that while these benefits have been associated with the paleo diet, research is ongoing and individual results may vary. Additionally, it’s important to work with a healthcare provider to ensure that any dietary changes are safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
II. What is the paleo diet?
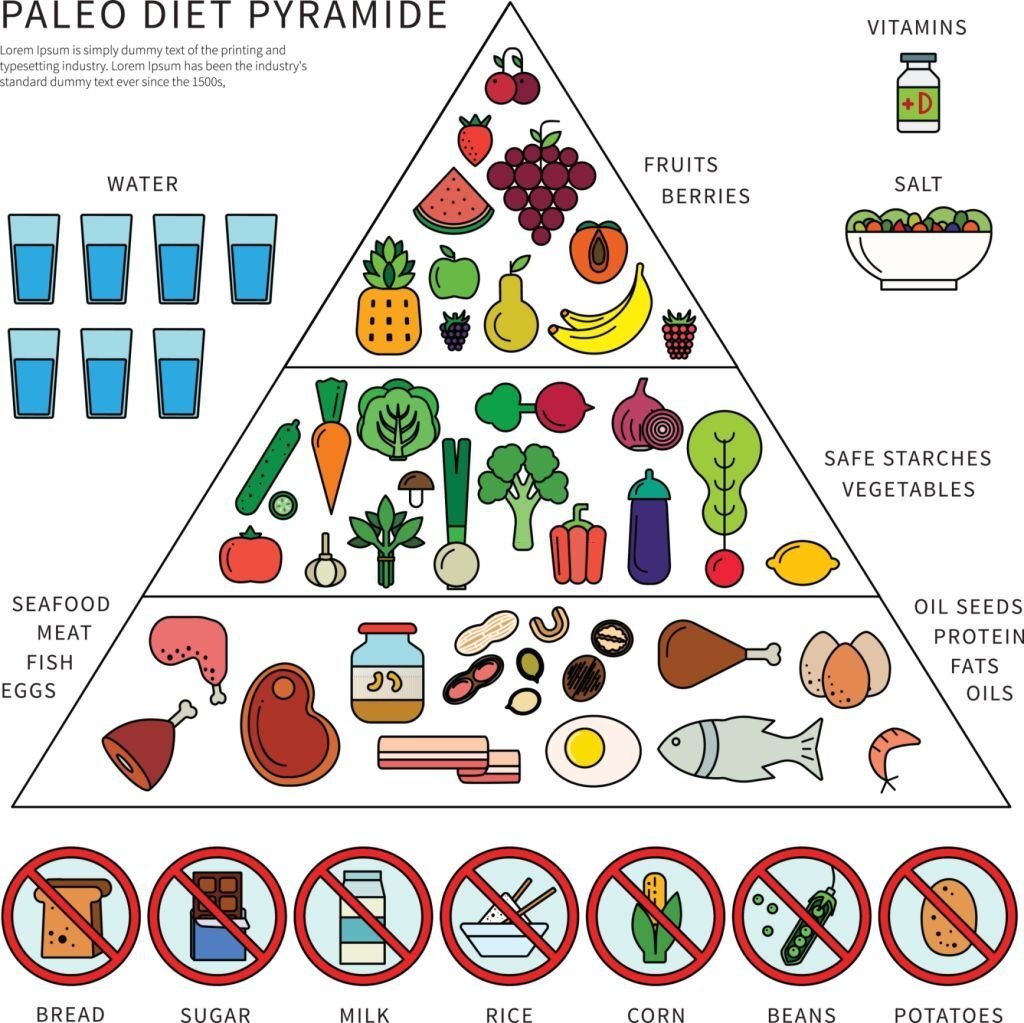
A. Explanation of the paleo diet principles
The paleo diet, also known as the Paleolithic or caveman diet, is a way of eating that mimics the dietary habits of our ancestors who lived during the Paleolithic era. The principle behind the diet is to consume whole, unprocessed foods that were commonly eaten during this time period, such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
The paleo diet is based on the belief that our bodies are better adapted to the types of food that were consumed by early humans during the Paleolithic era, which ended around 10,000 years ago with the advent of agriculture. This means that the paleo diet excludes processed and refined foods, dairy products, grains, legumes, and refined sugars, all of which were introduced into the human diet during the agricultural revolution.
Proponents of the paleo diet believe that it can help to improve overall health by reducing inflammation, improving digestion, increasing energy levels, and promoting weight loss. Additionally, the diet is believed to provide a range of nutrients that are essential for maintaining optimal health, including protein, healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
B. Foods allowed on the paleo diet
The paleo diet encourages the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods that were available to our ancestors in the Paleolithic era. Here are some of the foods allowed on the paleo diet:
- Meat: All types of meat are allowed, including beef, chicken, lamb, and pork.
- Fish and seafood: Wild-caught fish and seafood are recommended, as they are a good source of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Eggs: Eggs are allowed on the paleo diet, as they are a good source of protein and nutrients.
- Vegetables: All types of vegetables are allowed, especially non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and cauliflower.
- Fruits: Fruits are allowed in moderation, as they can be high in sugar. Berries, in particular, are a good option.
- Nuts and seeds: All types of nuts and seeds are allowed, but they should be consumed in moderation due to their high calorie content.
- Healthy fats: Healthy fats like olive oil, coconut oil, and avocado are encouraged on the paleo diet.
- Herbs and spices: Herbs and spices can be used to add flavor to meals without adding calories or unhealthy ingredients.
Examples of paleo-approved meats
- Beef
- Bison
- Chicken
- Duck
- Elk
- Fish (including salmon, trout, tuna, and mackerel)
- Game meats (such as venison, rabbit, and wild boar)
- Lamb
- Pork
- Turkey
It’s important to note that when selecting meat on the paleo diet, it’s best to choose grass-fed and pasture-raised options whenever possible, as these tend to be higher in nutrients and free of antibiotics and hormones.
Examples of paleo-approved vegetables
- Leafy greens: Kale, spinach, collard greens, Swiss chard, and lettuce.
- Cruciferous vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and bok choy.
- Root vegetables: Sweet potatoes, yams, carrots, parsnips, turnips, and beets.
- Nightshade vegetables: Tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, and potatoes (although some paleo followers avoid potatoes due to their high glycemic index).
- Other vegetables: Asparagus, green beans, zucchini, squash, onions, garlic, mushrooms, and artichokes.
It is important to note that while vegetables are a key component of the paleo diet, it is recommended to focus on non-starchy vegetables and to limit or avoid high-carbohydrate vegetables such as corn and peas.
Examples of paleo-approved fruits
- Berries (strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, blackberries)
- Apples
- Oranges
- Bananas
- Mangoes
- Pineapples
- Grapes
- Melons (watermelon, cantaloupe, honeydew)
- Peaches
- Plums.
It’s important to note that dried fruits and fruit juices are not recommended on the paleo diet as they can be high in sugar and lack the fiber of whole fruits.
Examples of paleo-approved fats and oils
- Avocado oil
- Coconut oil
- Olive oil
- Ghee (clarified butter)
- Animal fats (such as lard or tallow)
- Nut oils (such as macadamia or almond oil)
It’s important to note that when choosing oils on the paleo diet, it’s best to opt for those that are minimally processed and not hydrogenated. This means avoiding oils like canola or vegetable oil, which are heavily processed and can contain unhealthy trans fats.
Examples of paleo-approved nuts and seeds
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Cashews
- Pistachios
- Macadamia nuts
- Hazelnuts
- Pecans
- Brazil nuts
- Pine nuts
- Sunflower seeds
- Pumpkin seeds
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Sesame seeds
- Hemp seeds
It’s important to note that while nuts and seeds are generally considered paleo-friendly, they should be consumed in moderation as they are high in calories and can be easy to overeat. Additionally, some people may have allergies or intolerances to certain nuts and seeds, so it’s important to listen to your body and make adjustments as needed.
C. Foods not allowed on the paleo diet
The paleo diet excludes processed foods, grains, legumes, dairy, refined sugar, and vegetable oils. Here are some specific examples of foods not allowed on the paleo diet:
Examples of grains and legumes not allowed on the paleo diet
Grains:
- Wheat
- Rice
- Barley
- Corn
- Oats
- Rye
- Quinoa
- Buckwheat
- Millet
Legumes:
- Beans (black, kidney, navy, pinto, etc.)
- Lentils
- Peanuts
- Soybeans
- Chickpeas (garbanzo beans)
- Peas (including snow peas, sugar snap peas)
- Hummus
Examples of processed foods not allowed on the paleo diet
- Processed meats, such as hot dogs, sausages, and deli meats
- Fast food and fried foods
- Refined sugars and artificial sweeteners, such as high fructose corn syrup, table sugar, and aspartame
- Packaged snacks, such as chips and crackers
- Refined grains, such as white bread and pasta
- Vegetable oils, such as soybean oil, canola oil, and corn oil
- Dairy products, including milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Soft drinks and other sugary beverages
- Processed condiments, such as ketchup, mayonnaise, and salad dressings
- Processed desserts, such as cookies, cakes, and ice cream
Why these foods are not allowed
The paleo diet is based on the principle of consuming whole, unprocessed foods that are similar to what our ancestors may have eaten during the Paleolithic era. The foods that are not allowed on the paleo diet are typically those that are highly processed and have become a part of the modern diet in recent times.
Grains and legumes are not allowed on the paleo diet because they contain anti-nutrients, such as phytates and lectins, that can interfere with the absorption of important minerals and cause inflammation in the body. These foods also tend to be high in carbohydrates and can cause spikes in blood sugar levels.
Processed foods are not allowed on the paleo diet because they often contain additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients that are not beneficial for the body. These foods can also be high in refined carbohydrates, unhealthy fats, and salt, which can contribute to a range of health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
Overall, the paleo diet emphasizes the consumption of nutrient-dense foods that are in their natural state and promotes the avoidance of foods that can be detrimental to health.
III. The benefits of the paleo diet

A. How the paleo diet can lead to weight loss
The paleo diet can be an effective weight loss tool due to several reasons. First, the paleo diet promotes the consumption of nutrient-dense whole foods that are naturally low in calories. This means that individuals following the paleo diet can consume a larger volume of food while still maintaining a calorie deficit, which is necessary for weight loss.
Second, the paleo diet eliminates processed and high-sugar foods, which are major contributors to weight gain. Processed foods are often high in calories and low in nutrients, while high-sugar foods can spike blood sugar levels, leading to cravings and overeating.
Third, the paleo diet is high in protein, which can help individuals feel full and satisfied, reducing overall food intake. Protein is also important for building and maintaining muscle mass, which can increase metabolism and further aid in weight loss.
Finally, the paleo diet encourages regular physical activity, which is essential for weight loss and overall health. By combining a paleo diet with regular exercise, individuals can see significant weight loss results.
B. How the paleo diet can improve digestion
The paleo diet is rich in whole, unprocessed foods, and eliminates many of the processed and refined foods that can be difficult to digest. This can lead to improvements in digestion for many people.
For example, the paleo diet is typically high in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and nuts, which can help promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation. The diet also eliminates many common allergens, such as gluten and dairy, which can be a source of digestive discomfort for some people.
Furthermore, the paleo diet encourages the consumption of fermented foods, such as sauerkraut and kimchi, which are rich in probiotics that can help promote a healthy gut microbiome. This can improve digestion and overall gut health, which has been linked to a wide range of health benefits, including better immune function and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Overall, by emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods and eliminating many of the common culprits of digestive issues, the paleo diet can be a helpful tool for improving digestion and promoting overall gut health.
C. How the paleo diet can increase energy levels
The paleo diet can potentially increase energy levels due to its focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods. By avoiding processed and refined foods, which can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes, and instead consuming foods rich in protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates, the body can better maintain steady energy levels throughout the day.
Additionally, the paleo diet may help improve gut health, which can also contribute to increased energy levels. The diet emphasizes the consumption of fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, as well as probiotic-rich fermented foods, which can promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and improve digestion. When the gut is functioning optimally, nutrients are more effectively absorbed and utilized by the body, leading to increased energy levels.
D. How the paleo diet can reduce inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response by the body to fight off harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, injuries, or toxins. However, chronic inflammation can lead to a wide range of health problems, including autoimmune disorders, heart disease, and cancer.
The paleo diet is rich in whole, unprocessed foods that are high in nutrients and low in inflammation-causing substances, such as refined sugars, processed carbohydrates, and trans fats. By eliminating these inflammatory foods, the paleo diet can help reduce chronic inflammation in the body.
Furthermore, the paleo diet emphasizes the consumption of anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and fatty fish, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds. These foods have been shown to help reduce inflammation markers in the body.
Studies have shown that following a paleo-style diet can lead to significant reductions in inflammation in the body, which can help improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
E. How the paleo diet can improve overall health
The paleo diet has been shown to have several health benefits beyond weight loss and improved digestion. Here are some ways that following the paleo diet can improve overall health:
- Improved blood sugar control: The paleo diet eliminates processed foods and refined sugars, which can lead to spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, the paleo diet can help regulate blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Improved cholesterol levels: Studies have shown that the paleo diet can improve cholesterol levels, including reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol.
- Improved heart health: By reducing inflammation and promoting healthy blood sugar and cholesterol levels, the paleo diet can also lead to improved heart health and a reduced risk of heart disease.
- Increased intake of nutrient-dense foods: The paleo diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. By increasing the intake of these foods, the paleo diet can help ensure that the body is getting all the nutrients it needs for optimal health.
- Reduced exposure to toxins: The paleo diet encourages the use of organic and grass-fed animal products, as well as avoiding processed foods and additives. By reducing exposure to toxins and chemicals, the paleo diet can help improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
IV. Tips for following the paleo diet

A. Suggestions for meal planning and preparation
Tips for following the paleo diet:
- Plan ahead: Create a meal plan for the week and make a grocery list to ensure that you have all the necessary ingredients on hand.
- Focus on whole foods: When grocery shopping, stick to the outer edges of the store where you will find fresh produce, meats, and seafood.
- Cook at home: By preparing your meals at home, you have better control over the ingredients used and can avoid processed foods and unhealthy additives.
- Experiment with new recipes: To keep your meals interesting and flavorful, try new recipes that incorporate paleo-approved ingredients.
- Practice mindful eating: Slow down and savor your food, paying attention to how it makes you feel.
Suggestions for meal planning and preparation:
- Batch cook: Prepare large batches of proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats on the weekends to use throughout the week.
- Keep it simple: Many paleo meals can be prepared with just a few ingredients. Focus on simple, whole-food-based meals.
- Use paleo-approved condiments and spices: To add flavor to your meals, use spices and condiments such as olive oil, coconut aminos, and fresh herbs.
- Make use of leftovers: Don’t let leftovers go to waste. Use them for easy meals or to create new dishes.
- Use paleo-approved snacks: When hunger strikes between meals, choose paleo-approved snacks such as nuts, seeds, and fresh fruits and vegetables.
B. Tips for eating out while following the paleo diet
Here are some tips for eating out while following the paleo diet:
- Research the restaurant beforehand: Before going out to eat, research the restaurant’s menu online to see if they have any paleo-friendly options.
- Avoid bread and other grains: Most restaurants offer bread or other grain-based items before your meal. Avoid these items and instead ask for a side salad or other paleo-approved appetizer.
- Stick to simple dishes: Choose simple dishes with basic ingredients like grilled meat, fish, or vegetables. Avoid dishes with sauces, breading, or added sugars.
- Ask for modifications: Don’t be afraid to ask for modifications to a dish to make it more paleo-friendly. For example, ask for no cheese or croutons on a salad, or substitute a side of fries for a side of vegetables.
- Bring your own paleo-friendly snacks: If you’re unsure if there will be any paleo-friendly options at the restaurant, bring your own snacks like nuts or fruit.
- Be mindful of portion sizes: Restaurants often serve larger portions than what is recommended on the paleo diet. Consider splitting a meal with a friend or taking leftovers home.
- Don’t be too hard on yourself: Remember that it’s okay to indulge in non-paleo foods every once in a while. Don’t be too hard on yourself if you have a slip-up, and just get back on track with your paleo diet at your next meal.
C. Explanation of how to handle cravings while on the paleo diet
While following the paleo diet, it’s common to experience cravings for foods that are not allowed, such as processed snacks, sugary desserts, and other comfort foods. However, there are several strategies you can use to handle these cravings and stay on track with your paleo diet.
- Plan ahead: If you know you’ll be in a situation where tempting foods will be present, plan ahead by bringing your own paleo-friendly snacks or eating a meal beforehand to avoid getting too hungry.
- Focus on nutrient-dense foods: Make sure you’re getting plenty of nutrient-dense foods on the paleo diet, such as vegetables, fruits, lean meats, and healthy fats. These foods will keep you full and satisfied, reducing the likelihood of cravings.
- Find paleo-friendly substitutes: There are many paleo-friendly substitutes for common comfort foods, such as paleo-friendly baked goods or cauliflower rice instead of regular rice. Experiment with these substitutes to find ones that satisfy your cravings.
- Practice mindful eating: When you do have a craving, practice mindful eating by really savoring the food and paying attention to how it makes you feel. This can help you be more mindful of your food choices overall and reduce the likelihood of giving in to cravings in the future.
- Allow for occasional indulgences: It’s important to remember that the paleo diet is not meant to be overly restrictive or punishing. Allow yourself to indulge in your favorite non-paleo foods occasionally, in moderation, to avoid feeling deprived and increase the likelihood of long-term success on the diet.
D. Discussion of potential challenges and how to overcome them
The paleo diet can come with some challenges, particularly for those who are used to a diet rich in processed foods and grains. Here are some potential challenges and tips for overcoming them:
- Cost: The paleo diet can be more expensive than a standard diet because it emphasizes high-quality, whole foods. To save money, consider buying in bulk and choosing less expensive cuts of meat. You can also look for local farmers markets or community-supported agriculture programs for fresh, locally sourced produce.
- Time: Preparing paleo-friendly meals can take more time than grabbing a quick processed snack. To save time, consider meal prepping for the week, batch cooking, or using a slow cooker to make meals while you’re at work.
- Social situations: Eating out or attending social events where food is served can be challenging on the paleo diet. Look at menus ahead of time and choose restaurants that offer paleo-friendly options. If you’re attending a social event, consider bringing your own paleo-friendly dish to share.
- Cravings: It’s natural to experience cravings for processed foods or sugar when starting the paleo diet. To combat cravings, make sure you’re eating enough nutrient-dense foods and staying hydrated. You can also try paleo-friendly alternatives to your favorite treats, such as using almond flour to make baked goods or eating fruit as a sweet snack.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Cutting out entire food groups can lead to potential nutrient deficiencies, so it’s important to make sure you’re getting enough of essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and iron. Consider incorporating paleo-friendly sources of these nutrients into your diet, such as leafy greens, nuts, and seafood.
By being aware of these potential challenges and following these tips, you can successfully navigate the paleo diet and reap its many health benefits.
V. Criticisms of the paleo diet
A. Explanation of common criticisms of the paleo diet
The paleo diet has been a topic of controversy in the nutrition world, with some experts praising its benefits and others criticizing its restrictions and potential risks. Some of the common criticisms of the paleo diet include:
- Lack of scientific evidence: Critics argue that there is limited scientific evidence to support the health benefits of the paleo diet.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Because the paleo diet restricts certain food groups, such as grains and legumes, it can be challenging to get enough nutrients, such as fiber, calcium, and vitamin D.
- Cost: The paleo diet can be expensive, as it promotes the consumption of high-quality, organic, and grass-fed meats, which can be more costly than conventionally raised meats.
- Unsustainable: Critics argue that the paleo diet’s emphasis on animal products is not sustainable for the environment or for public health, as it contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and can increase the risk of chronic diseases.
- Potential risks: Some experts warn that the paleo diet’s high protein and fat content can increase the risk of kidney disease and other health problems.
It is important to note that while there may be some valid concerns about the paleo diet, many of these criticisms can be addressed through careful meal planning and monitoring of nutrient intake. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary changes.
B. Discussion of the validity of these criticisms
There are several common criticisms of the paleo diet that are worth considering. One criticism is that it is difficult to follow, as it requires significant changes in eating habits and may be more expensive than a typical Western diet. Additionally, some critics argue that the paleo diet lacks sufficient scientific evidence to support its health claims.
In response to these criticisms, it is important to note that any dietary change can be difficult to implement, especially if it involves a significant shift in eating habits. However, with proper planning and preparation, following a paleo diet can be a sustainable and satisfying lifestyle choice.
As for the lack of scientific evidence, it is true that there is still ongoing research in this area. However, a growing body of evidence suggests that the paleo diet can have numerous health benefits, including weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and reduced inflammation. Furthermore, many of the foods recommended on the paleo diet are whole, nutrient-dense foods that have been associated with improved health outcomes in numerous studies.
Overall, while there may be some valid criticisms of the paleo diet, the available evidence suggests that it can be a healthy and effective dietary approach for many individuals. As with any dietary change, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if the paleo diet is right for you.
C. Explanation of potential risks associated with the paleo diet
While the paleo diet is generally considered safe for most people, there are some potential risks that should be considered. Here are some of the main ones:
- Nutrient deficiencies: Eliminating certain food groups from your diet can increase the risk of nutrient deficiencies if you’re not careful. For example, if you don’t eat enough dairy or leafy greens, you may not get enough calcium or vitamin K.
- High meat consumption: While the paleo diet emphasizes protein from animal sources, consuming too much meat can increase the risk of certain health problems, such as heart disease and some types of cancer.
- Difficulty sticking to the diet: Some people find it challenging to stick to the strict guidelines of the paleo diet, which can lead to frustration and ultimately giving up on the diet altogether.
- Cost: The paleo diet can be more expensive than a typical diet, as it emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, some of which can be pricier.
- Sustainability: Some critics argue that the paleo diet is not sustainable on a large scale, as it would require significant changes to the way our food system currently operates.
It’s important to note that these risks can be mitigated with careful planning and attention to your nutrient intake. It’s also a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new diet.
VI. Conclusion
A. Recap of the benefits of the paleo diet:
Overall, the paleo diet emphasizes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods that are nutrient-dense and high in protein. By eliminating processed and refined foods, the paleo diet may lead to weight loss, improved digestion, increased energy, and reduced inflammation. Additionally, the paleo diet may improve blood sugar control, cholesterol levels, and heart health.
B. Why the paleo diet may be a good option for some individuals:
The paleo diet may be a good option for individuals who want to improve their overall health by consuming a nutrient-dense, whole food diet. It may be particularly beneficial for those with certain health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or digestive issues. The paleo diet may also be a good option for athletes or individuals looking to improve their athletic performance, as the diet emphasizes the consumption of high-quality protein.
C. Final thoughts on the paleo diet and its potential impact on health:
While the paleo diet may offer numerous health benefits, it is important to remember that it may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, some critics argue that the paleo diet may be too restrictive and difficult to follow long-term. It is important to listen to your body and consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary changes.
In conclusion, the paleo diet may be a good option for individuals who want to improve their overall health by consuming a nutrient-dense, whole food diet. While it may have its limitations and potential risks, the paleo diet has been shown to offer numerous health benefits for many individuals.
